Hydrogen-Fueled Vehicles
How They Work, Their Potential, and Whether They Are Truly Worth It
Introduction
As the world searches for cleaner alternatives to fossil-fuel vehicles, hydrogen-fueled vehicles have emerged as a promising but debated solution. They offer zero tailpipe emissions, fast refueling, and long driving range—but also face infrastructure, cost, and efficiency challenges.
So the key question is not only how hydrogen vehicles work, but also whether they are practical and worth adopting today.
What Is a Hydrogen-Fueled Vehicle?
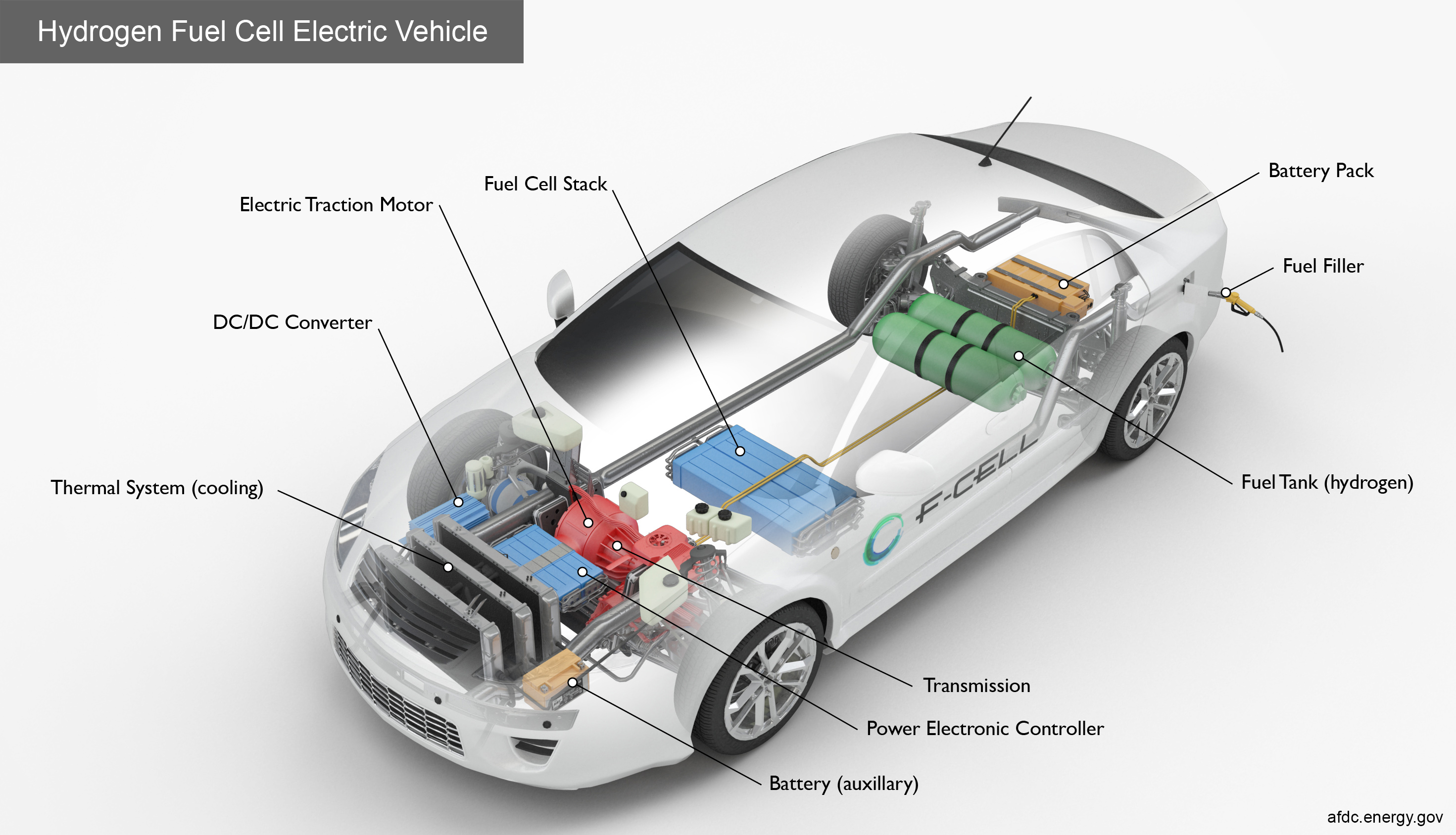
A hydrogen-fueled vehicle is typically a Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV). Instead of burning fuel like petrol or diesel engines, it uses hydrogen gas to generate electricity through a chemical reaction.

Well-known examples include the Toyota Mirai and the Hyundai NEXO.
How a Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Works
Step-by-Step Process
Hydrogen Storage
Hydrogen gas is stored in high-pressure tanks (typically 700 bar).
These tanks are engineered to be extremely strong and safe.
Fuel Cell Reaction
Hydrogen is fed into a fuel cell stack.
Oxygen from the air enters the system.
A chemical reaction occurs:
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Electricity + Heat + Water
Electric Power Generation
The electricity produced powers an electric motor.
A small battery or capacitor stores excess energy.
Vehicle Movement
The electric motor drives the wheels.
The only exhaust emitted is water vapor.
This makes hydrogen vehicles zero-emission at the tailpipe.
Key Advantages of Hydrogen-Fueled Vehicles
1. Zero Tailpipe Emissions
No CO₂, NOx, or particulate pollution
Only water vapor is released
2. Fast Refueling
Refueling takes 3–5 minutes, similar to petrol cars
Much faster than charging most electric vehicles
3. Long Driving Range
Typical range: 500–650 km per tank
Comparable to conventional vehicles
4. Smooth and Quiet Operation
Electric drivetrain ensures low noise and vibration
Major Challenges and Limitations
1. Hydrogen Production Is Not Always Clean
Most hydrogen today is produced from natural gas (called grey hydrogen), which releases CO₂. Truly clean hydrogen (green hydrogen) requires renewable electricity and is still expensive.
2. Infrastructure Is Extremely Limited
Very few hydrogen refueling stations worldwide
Almost nonexistent in many countries
3. High Cost
Vehicles are expensive
Hydrogen fuel itself is costly
Infrastructure investment is massive
4. Energy Efficiency Issues
Hydrogen vehicles lose energy at multiple stages:
Electricity → Hydrogen (electrolysis)
Compression and transport
Conversion back to electricity
Overall efficiency is lower than battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
Hydrogen Vehicles vs Battery Electric Vehicles (EVs)
| Aspect | Hydrogen Vehicle | Battery EV |
|---|---|---|
| Refueling / Charging | Very fast | Slower |
| Infrastructure | Very limited | Rapidly expanding |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Vehicle Cost | Very high | Decreasing |
| Best Use Case | Long-distance, heavy use | Daily urban & suburban use |
Where Hydrogen Makes More Sense
Hydrogen is often more practical for:
Heavy trucks
Buses
Trains
Ships
Industrial transport
For personal cars, battery EVs currently have a strong advantage.
Is Hydrogen-Fueled Mobility the Future?
Short Answer: Not yet for most people
Long Answer:
Hydrogen vehicles are technologically impressive, environmentally promising, and strategically important—but not ready for mass adoption in passenger cars.
They may become viable if:
Green hydrogen becomes cheap
Infrastructure expands significantly
Production efficiency improves
Until then, hydrogen is better viewed as a long-term complementary solution, not a replacement for electric vehicles.
Final Verdict: Is It Worth It?
✔ Worth it for:
Research and development
Heavy and commercial transport
Countries investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure
✖ Not worth it (currently) for:
Average private car owners
Regions without hydrogen stations
Cost-sensitive markets
Conclusion
Hydrogen-fueled vehicles represent an important chapter in clean mobility—but they are not a silver bullet. While they offer zero emissions at the vehicle level, real-world challenges limit their practicality today.
The future of transportation will likely be multi-technology, where hydrogen, battery electric, and other solutions coexist—each used where it makes the most sense.
Innovation must be guided not just by possibility, but by efficiency, accessibility, and real-world impact.
Support This Work
This blog is created to share free, educational, and awareness-based content on science, technology, and sustainable futures.
If you found this article useful and wish to support the continuation of this service, you may contribute voluntarily using the link below.
👉 Support via PayPal:
https://www.paypal.com/ncp/payment/G5LPGXG437DUL
Explore More
🔗 Read more science, engineering, and future-tech articles:
👉 https://craarts.blogspot.com
🎨 Explore technology and educational visuals:
👉 https://www.shutterstock.com/g/craarts

achhi jankari hain ise follow karna chahiye
ReplyDelete